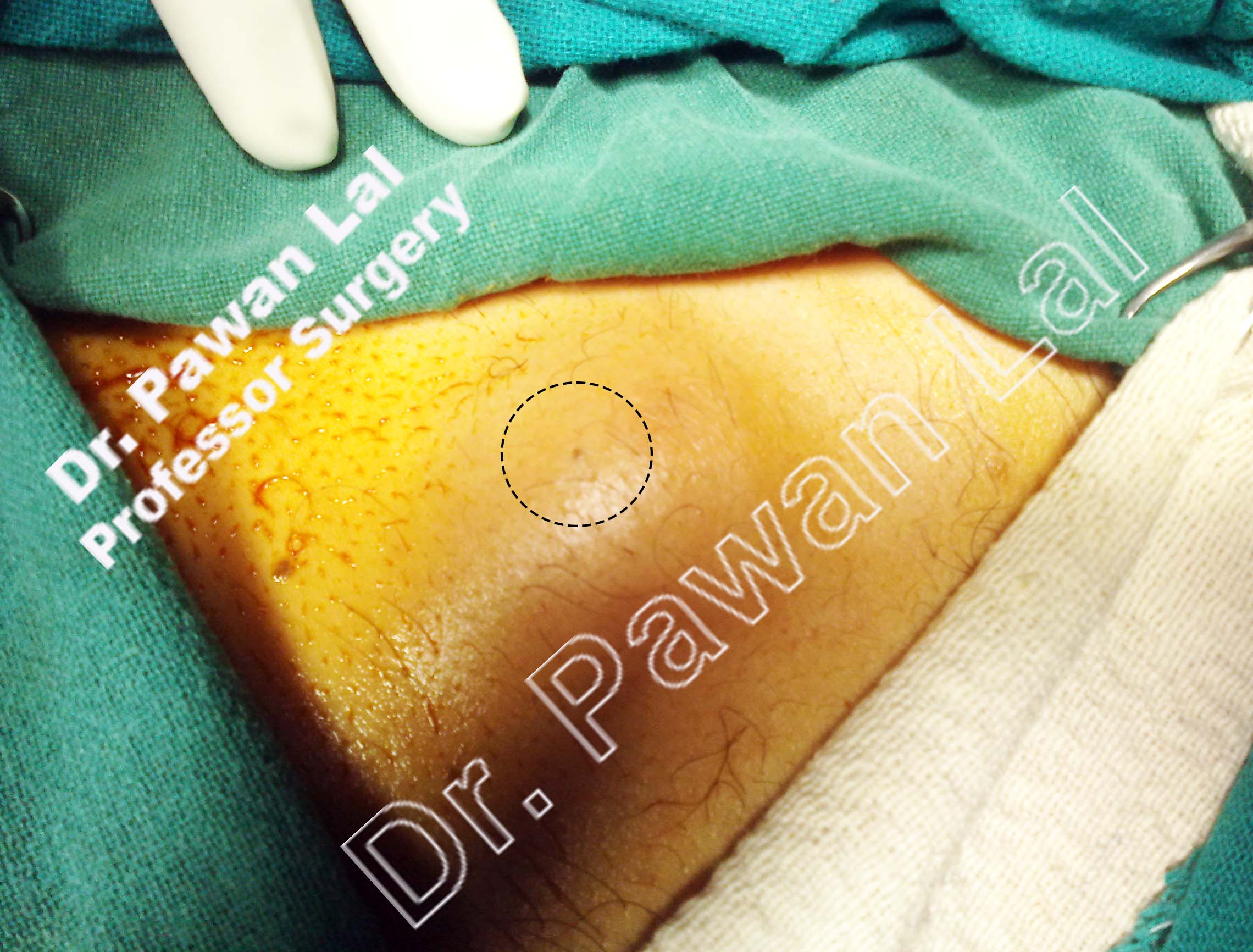
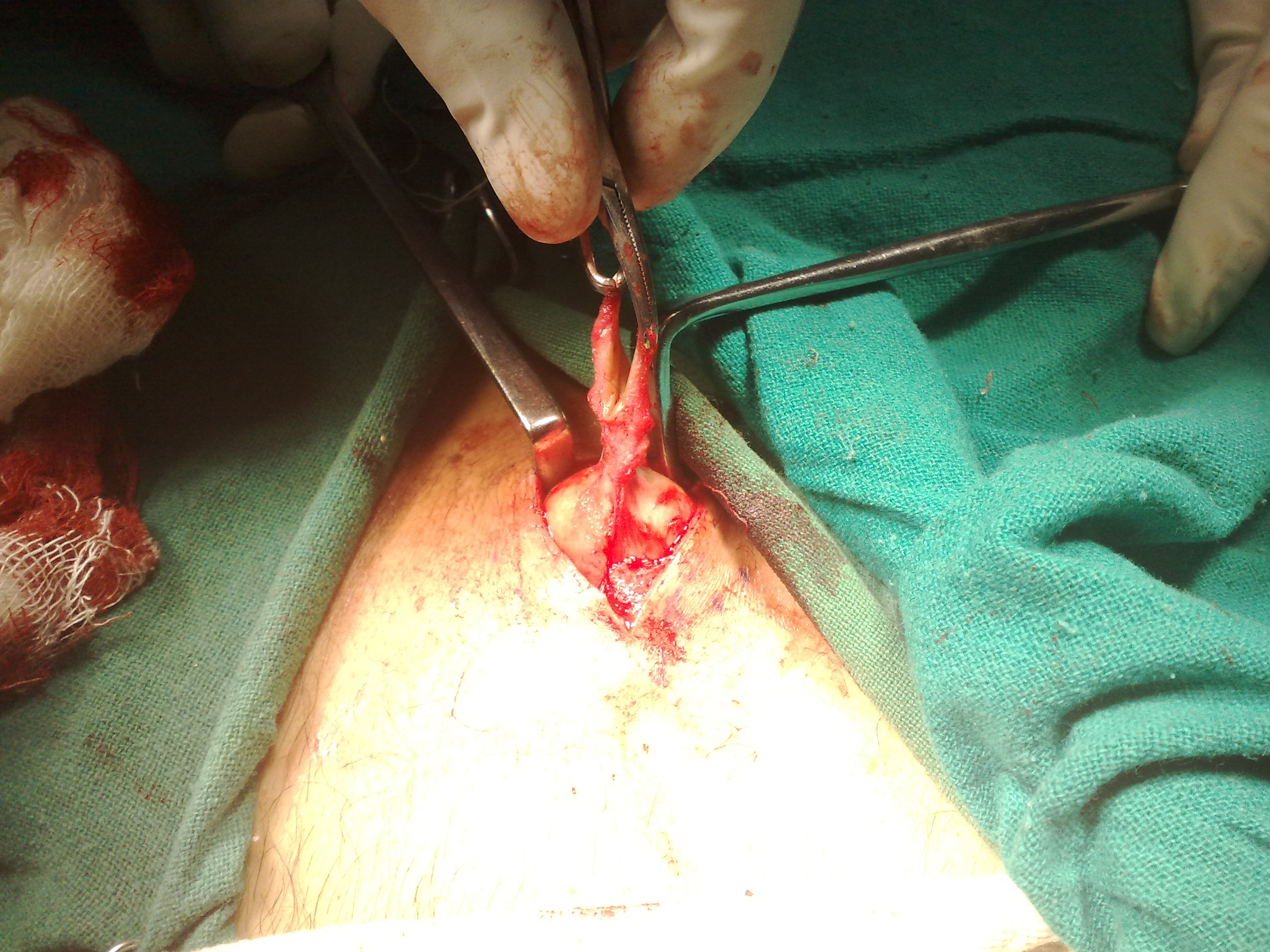
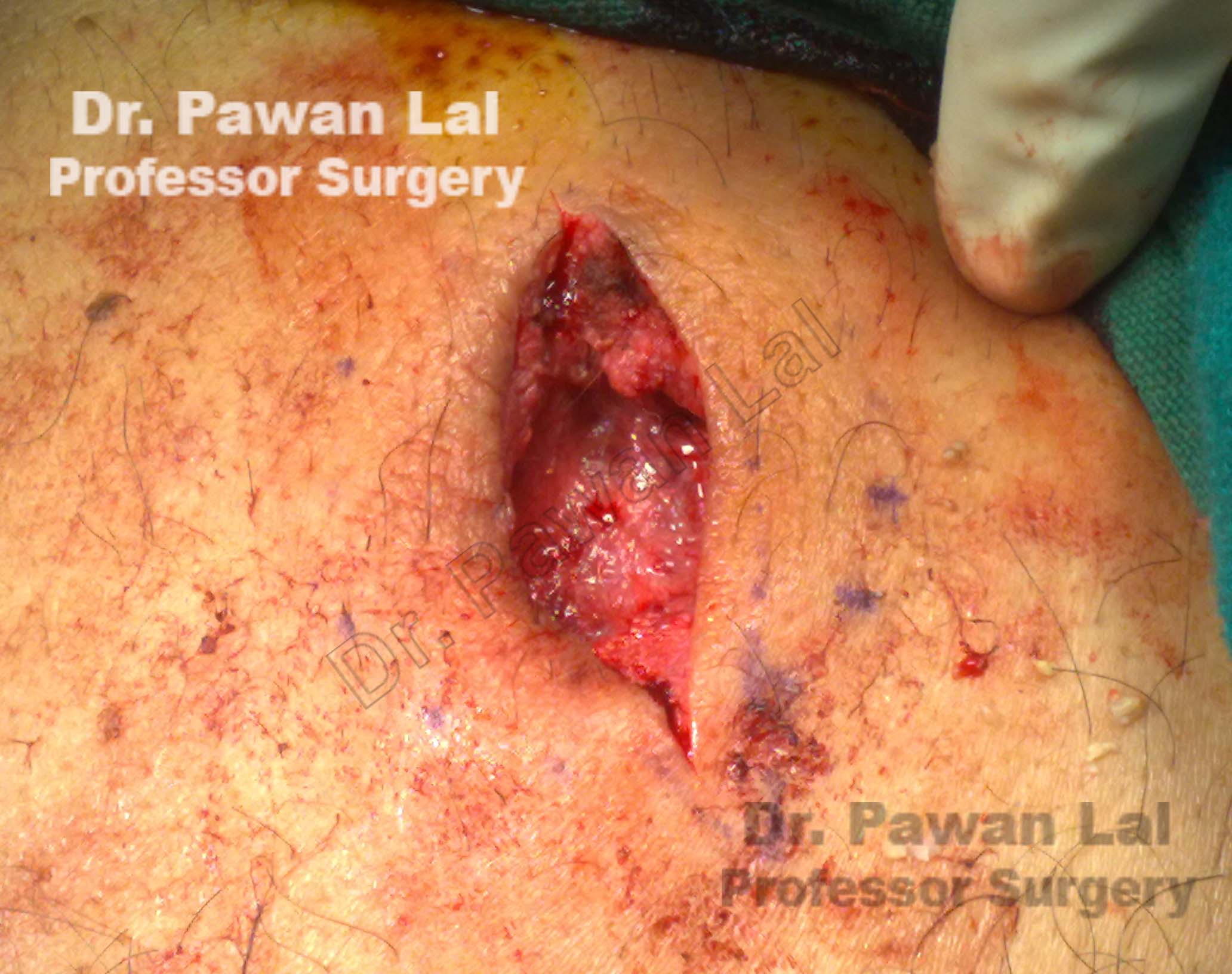
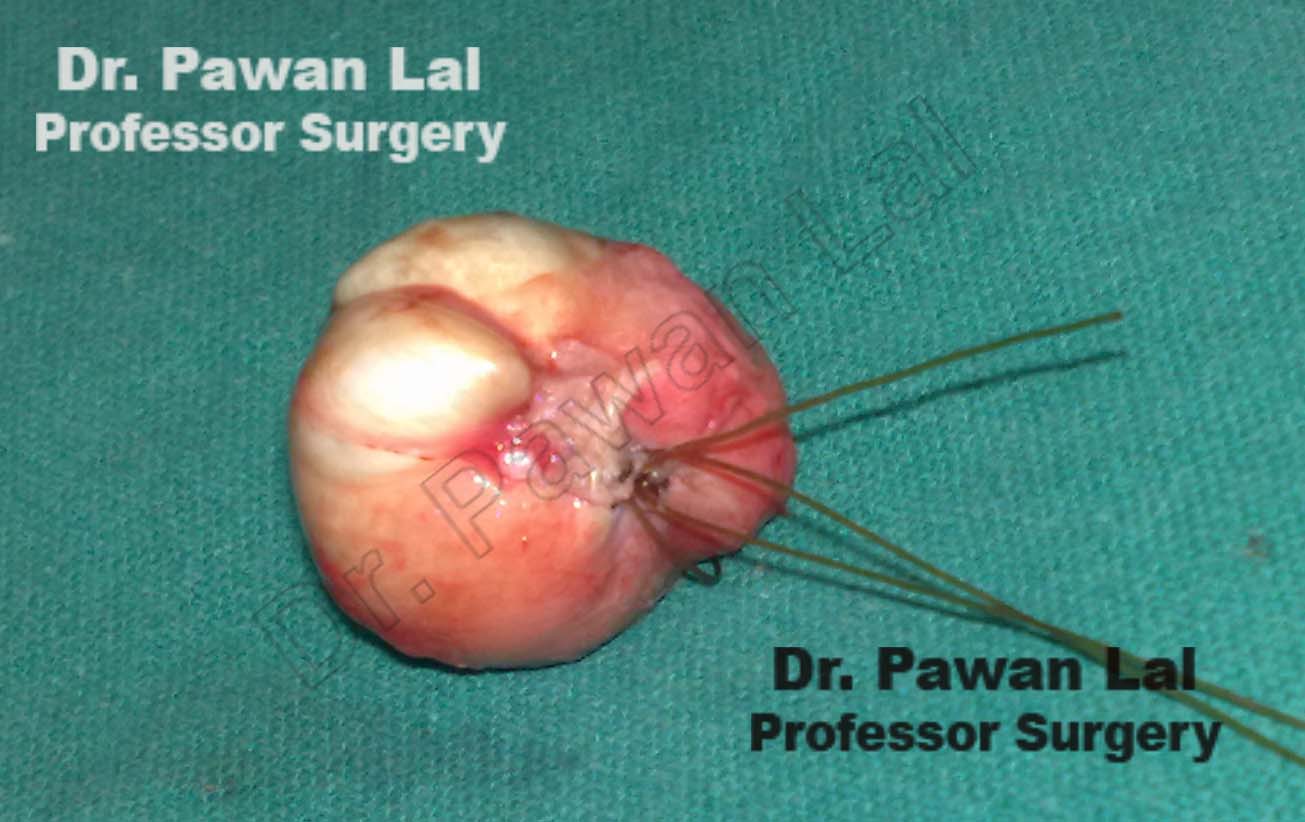
Scrotal Sebaceous Cysts
(Also called as Trichilemmal cyst (TC), or pilar cyst of the scrotum wall)
usually confused with epidermal cysts of scrotum which are differentiated with the relatively thicker contents of the cysts.
Approximately 1% of sebaceous cysts undergo the malignant transition to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and basal cell carcinoma (BCC)1.
When the sebaceous duct becomes clogged and keratinous material, hair follicles, and debris gather within the gland, a sebaceous cyst forms. Trauma, illness, frequent hair combing, or congenital sebaceous duct development abnormalities can all lead to the formation of sebaceous cysts.
They can occur because of epidermal rest sequestration during embryonic life, blockage of the pilosebaceous unit, or the traumatic or surgical implantation of epithelial elements. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure, and eccrine duct blockage may also cause Palmoplantar ECs. There are several ideas that contend that ECs may have an embryonic origin from teratomas formed from germ cells, ectopic tissue derived from nearby regions, or traumatic implantation of epidermal tissue into the dermis.
A single cyst is referred to as sebaceous, whilst many cysts are referred to as TCs.

The scrotal sebaceous cysts can vary from single cyst to few cysts to
multiple cysts completely covering the scrotal skin

Scrotal calcinosis
Cutaneous calcium salt deposits are hard papules and nodules formed by the deposition of insoluble calcium salts in the skin tissue of the body2. At present, the pathogenesis of idiopathic calcinosis of the scrotum is not clear. Possible pathogenesis includes parasites, foreign bodies, and malnutrition leading to calcification.
scrotal idiopathic calcium salt deposits are multiple nodules of scrotal skin with no cause, hardness, no family history, and skin rupture that can discharge cheese like gravel particles.
References
- Sahito AM, Sehar A, Kumari U, Daggula NR, Kumari S, Khoshbakht F. Scrotal trichilemmal cysts: a case report. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Apr 14;85(5):2166-2168. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000666. PMID: 37229016; PMCID: PMC10205296.
- Feng L, Shulin G, Jinhua W, Zhongxiang L, Peiyan L, Yanhua W, Jiangping X. Idiopathic calcinosis of scrotum: A case report and review of the literature. Heliyon. 2022 Sep 28;8(9):e10762. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10762. PMID: 36200019; PMCID: PMC9529499.
Sebaceous gland
- They secrete an oily substance called sebum (Latin, meaning fat or tallow) that is made of fat (lipids) and the debris of dead fat-producing cells. A branched type of Acinar gland, these glands exist in humans throughout the skin except in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
- Sebum acts to protect and waterproof hair and skin, and keep them from becoming dry, brittle, and cracked. It can also inhibit the growth of microorganisms on skin.
- Sebaceous glands can usually be found in hair-covered areas where they are connected to hair follicles to deposit sebum on the hairs, and bring it to the skin surface along the hair shaft.
- The structure consisting of hair, hair follicle and sebaceous gland is known as pilosebaceous unit.
- Sebaceous glands are also found in non haired areas of lips, eyelids, penis, labia minora and nipples; here the sebum reaches the surface through ducts.
- In the glands, sebum is produced within specialized cells and is released as these cells burst; sebaceous glands are thus classified as holocrine glands
Sebum
- Sebum is odorless, but its bacterial breakdown can produce odors. Sebum is the cause of some people experiencing "oily" hair if it is not washed for several days. Earwax is partly sebum.
- The composition of sebum varies from species to species; in humans, the lipid content consists of about 25% wax monoesters, 41% triglycerides, 16% free fatty acids, and 12% squalene.
- Sebaceous cyst
- Alternative names - Epidermal cyst; Keratin cyst; Epidermoid cyst
- Sebaceous cysts are sacs just beneath the skin that are filled with an oily, white, semisolid material called sebum
- Duct obstruction of a sebaceous gland in the hair follicle can result in a long, narrow channel opening in the surface comedo
Sebacous Cysts also called as Epidermoid cyst - forms due to obstruction of the duct of the sebaceous gland.
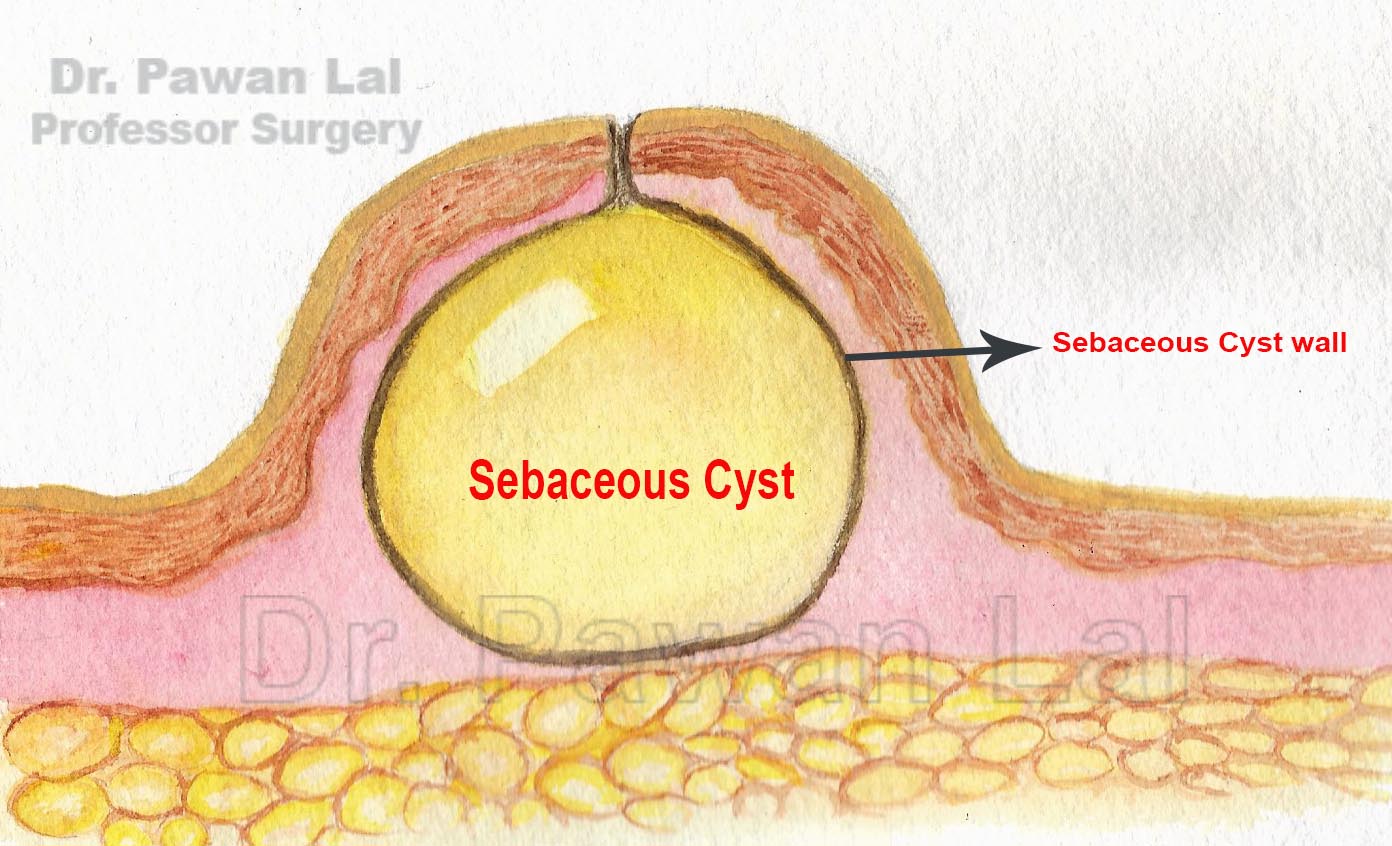
Treatment of Sebacous Cyst is Excision